Slack can be a phenomenal project management tool. While you can use it to organize your team, it’s designed for team communication and collaboration. Use Slack to supplement a more traditional project management system, but don’t rely on it fully to make your team more agile and flexible. Find the latest Insider Activity data for Slack Technologies, Inc. Class A Common Stock (WORK) at Nasdaq.com. Slack Time in Project Management Slack time, used in Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT), denotes how much an activity can be delayed beyond its earliest start date, without causing any problems in the completion of the project by its due date. Total slack: The total slack of an activity is the time this activity can be delayed without impact on the finish date of the project. The Critical Path methodology identifies the paths of tasks most likely to impact the project completion date.
Slack time: – It is necessary to remember that there occur only single longest path in the network and the other paths are being shorter than that length or equal to that length. Therefore, the activities and events should be finished before the actually required time. Slack time is referred as the time difference between the required date to fulfill critical path and the scheduled completion date. The event 4 is not on the crucial path in the following figure.
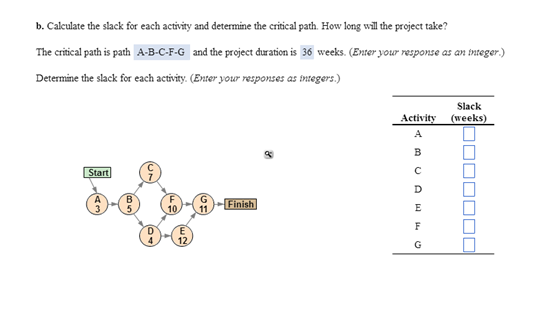
Simplified PERT Network
Seven weeks are required to go from event 2 to event 5 on the critical path by taking the route 2, 3, 5. Only four weeks are needed if the route 2, 4, 5 is adopted. Therefore three weeks are required if route 2-4-5 is adopted. Therefore event 4 should begin anywhere between zero to three weeks because it needs two weeks for completion after event 2 is completed. Another use for resources of people, facilities, money and equipment needed to finish event 4 must be searched by the management during these three weeks.
Therefore for resource allocation and scheduling as the critical path is important, because those events that are not on critical path for achievement can be rescheduled by the project manager with the coordination from the functional manager, during other time periods when maximum utilization of resources can be accomplished under the provision that the critical path time is not extended. Better balance of resources throughout the company is provided by this type of rescheduling through the utilization of slack times. Even by eliminating waiting or idle time, project costs may possibly reduce.
Slack Terminology
The difference between the latest permit able date and the earliest expected data on the basis of the following nomenclature is said to be slack.

TE = the earliest date (time) on which an event can be anticipated to happen
TL = without extending the completion date of the project, the latest date on which an event can occur
Slack Time = TL – TE
Slack Time Formula & Calculation in Project Management
The calculation for slack time is conducted for every event in the network as shown in the following figure by recognizing the latest starting date and the earliest expected date. TL – TE = 0 for event 1.
PERT Network with Slack Time
The reference point for the network can be served as the event 1 and can be easily specified as a calendar date. Bold line represents the critical path as before. There is no slack (i.e. TL = TE) for the events on the critical path and boundaries for events of noncritical path are also provided. For event 5 TL = TE x 3 + 7 = 10, since event 2 is important one. Critical path is terminated by the event 6 with a completion time of 15 weeks.
The earliest time for event 3 would be two weeks (TE = 0 + 2 = 2), which is not on critical path considering that it started as quickly as possible. By subtracting the time needed to finish the activity from events 3 to 5 from the latest beginning date of event 5 the latest allowable date is acquired.
Due to this fact, TL (for event 3) = 10 – 5 = 5 weeks. Now event 3 may happen anywhere between weeks 2 and 5 without disturbing the planned finishing date of the project. Event 4 can be applied the same procedure in which situation TL = 9 and TE = 6.
A simple PERT network is included in the above mentioned diagram and therefore slack time calculation is not much difficult. The earliest beginning dates should be ascertained by proceeding from start to completion through the network, for complex networks including multiple paths. Similarly by working backward from completion to beginning, the latest allowable beginning date should be calculated.

Comparison Models for a Time Phase PERT Chart
It should be cleared that the significance of recognizing clearly where the slack persistence cannot be overstated. Better technical performance is permitted by the effective use of the slack time. It is finding by the Donald Marques that organizations that effectively employ slack time were 30% more successful than the average in accomplishing technical needs.
Because of slack times, PERT networks are mostly not plotted with a time scale. There can be a requirement for the planning requirements that the PERT charts be rebuilt with time scales, in which situation a decision should be taken either to wish late or early time requirements for slack variables. The above figure represents this by comparing manpower planning with total program costs. In this figure early time requirements for slack variables are used.
The profitability of successfully meeting the schedule is ascertained by combining the earliest time and late time. In the table below, a sample of the needed information is highlighted.
The latest and earliest times are regarded as random variables. The actual schedule indicates the schedule for event occurrences that were built at the start of the project. In this table the last column provides the profitability regarding the earliest time will not surpass the actual schedule time for specific event.
In the example represented above, for every event the latest times and earliest times were calculated. The earliest and latest times were preferably evaluated for every activity instead. Additionally, the latest and earliest times were recognized merely as the date or time when an event may be anticipated to occur. Following four values need to be identified in order to make full use of the capabilities of the PERT Analysis / CPM.
- Earliest time when an activity may start (ES)
- Latest time when an activity may start (LS)
- Earliest time when an activity may finish (EF)
- Latest time when an activity may finish (LF)
The earliest and latest times recognized on the activity are shown in the following figure
A forward pass through the network should be made in order to evaluate the earliest starting times (i.e. left to right).The latest of the earliest finish dates of the predecessor activity is actually the earliest starting time of a successor activity. The total of the earliest starting time & activity duration is the latest starting time.
A backward pass through the network should be made by evaluating the latest finish time in order to calculate the finishing time. The latest starting time can be evaluated by subtracting the activity time from the latest finishing time since the activity time is known. The earliest finishing time of activities exiting the node is the latest is the latest finishing time for an activity entering a node.
For a typical network, the earliest & latest starting & finishing times are shown in the following figure
Typical PERT Chart with Slack Times
Slack Identification
For the project manager the slack identification is quite significant as it function as an early warning system. For example, if the available total slack time starts to diminish from specific reporting duration to the next that might point out that more highly skilled labor is required or longer than forecasted time is taken by the work. A new critical path might be building.
Slack time can be identified by looking at the earliest and latest start & finish times. Below is the example of the two cases that should be considered.
The slack time is easily recognized as four work units in situation a, where the work units can be expressed in months, weeks days or hours. This is said to be negative float or negative slack.
In order to understand the answer of the question that what can cause the slack to be negative. Following figure in helpful for this purpose.
Slack Time
Slack Activity Time
Work is done from left to right beginning at the customer’s starting milestone (position 1), when conducting a forward pass through a network. The backward pass, on the other hand, do not starts at where the forward pass ends but at the customer’s end date milestone (position 2). It is possible to have slack on the critical path if the forward pass ends at position 3 which is before the customer’s end date.
The slack time is mostly referred to as reserve time and may be filled with other activities or combined with activities like report writing in order to extend the forward pass to the customer’s completion date.
It is important to note that when the forward pass extends beyond the customer’s end date, negative slack normally occurs as represented by position 4 in above diagram. However customer’s completion date is still used to measure the backward pass, thus forming negative slack. This is probably to result when
Slack Show Activity
- When the actual plan was very optimistic but unrealistic
- During project execution one or more activities slipped
- The correct skill level has not been possessed by the assignment resources
- The customer’s end date was not realistic
- Until a later date, the needed resources would not be available
What Is Total Slack
Negative slack is an early warning indicator in any event. The customer’s end date is required to be maintained as corrective action indicated by early warning indicator.
