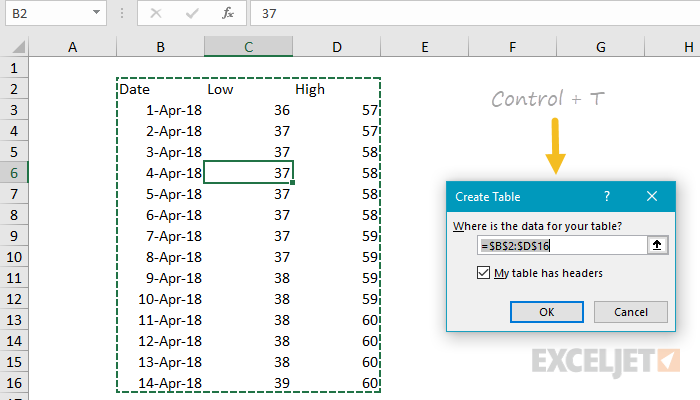
Create a Table With Style. If you’d like to use a fancy color scheme, follow along with this method to create your table. Select the range of cells in your spreadsheet that you want to convert to a table and open the “Home” tab. Click the “Format as Table” drop-down box in the ribbon and choose the style you’d like to use. Download latest version of Microsoft Excel for Windows. Safe and Virus Free. How to set Excel as default app to open.xls data files: Select the Windows Icon in the start bar. In the Search Bar, type 'Default Programs.' Click 'Default Programs.' Wait for the app to start, then select 'Set your default programs.' Find desired Excel version in the list. Select desired Excel version and select 'Set this program as default.'
1.1 ABSTRACT
This document defines the format of Uniform Resource Identifiers (URIs) for office productivity applications. The scheme is supported in Microsoft Office 2010 Service Pack 2 and later, including the Microsoft Office 2013 for Windows and the Microsoft SharePoint 2013 products. It is also supported in Office for iPhone, Office for iPad, and Office for Mac 2011.
1.2 INTRODUCTION
These URI schemes allow for office productivity applications to be invoked with various commands. Each application is given a different named scheme but all schemes follow the same rules for how the URI is formed (URI Schema).
1.3 URI SCHEMA
Full schema
< scheme-name >:< command-name >'|'< command-argument-descriptor > '|'< command-argument >
A URI as defined in this document may have one or more command arguments, each of which must include both the < command-argument-descriptor > and the < command-argument > elements and be delimited by the vertical bar ('|') character. When more than one command argument is included in a URI there must be a vertical bar ('|') character separating each command argument from the following command argument.
These schemes do not include an authority component as defined in section 3.2 of RFC 3986. Invocation of the commands specified in this document takes place in the context of the system invoking the command. For example, when the URI 'ms-excel:ofv|u|https://contoso/Q4/budget.xls' is invoked from a personal computer running Microsoft Windows with Microsoft Office 2013 installed the expected result is that the local installation of Microsoft Excel will be launched and passed arguments to open the file at https://contoso/Q4/budget.xls in read-only mode. Note that the vertical bar used as a delimiter in this specification is not among those characters identified in section 2.2 of RFC 3986 as reserved for potential use as delimiters. This is done intentionally to maximize the set of characters the URI command argument can support without a need to percent-encode those characters.
The scheme syntax includes the following:
< scheme-name >: This refers to the type of application that should be invoked. For instance, the ms-word: scheme name is registered by Microsoft Word.
':' separator
< command-name >: This describes the actions that the application should perform. For instance, opening a document for viewing. The list of command names is described in section 1.5.
'|' (vertical bar) separator
< command-argument-descriptor >: This element gives more information about what the command argument is about.
'|' (vertical bar) separator
< command-argument >: The arguments vary depending on the command. One common argument is the URI to a document, typically using the http or https scheme. Note that within < command-argument > segments the RFC 3986 reserved characters ':' and '/' are part of the argument data, not delimiters, and are therefore included unescaped.
Abbreviated schema
An abbreviated form of the office URI schemes allows for a more compact request to launch a specified Office application to open the resource located at a given URI. This abbreviated form implies the < command-name > 'ofv' and the < command-argument-descriptor > 'u'. No further commands or command arguments are allowed in this schema.
< scheme-name >:< command-argument >
< scheme-name >: the type of application that should be invoked. For instance ms-word: for Microsoft Word.
< command-argument >: URI for the resource the application should open. Currently only URIs based on the http or https scheme are supported.
1.4 SCHEME NAMES AND OFFICE APPLICATION REGISTRATIONS
The following is the list of scheme names implemented in Microsoft Office applications. When Microsoft Office is installed, each scheme name is registered with Windows to be handled by the Office product of the same name. Note that 'ms-spd' is an abbreviation for SharePoint Designer.
- ms-word:
- ms-powerpoint:
- ms-excel:
- ms-visio:
- ms-access:
- ms-project:
- ms-publisher:
- ms-spd:

- ms-infopath:
1.5 COMMANDS AND REQUIRED COMMAND ARGUMENTS
View Document
The following command will cause the application to open the document referenced by the URI in a read-only or view mode.
Command Name: ofv
Command argument descriptor: u
Command argument: a URI to the document, based on the http or https scheme
Example: ms-excel:ofv|u|https://contoso/Q4/budget.xls
Edit Document
The following command will cause the application to open the document referenced by the URI in editing mode.
Command Name: ofe
Command argument descriptor: u
Command argument: a URI to the document, based on the http or https scheme
Example: ms-powerpoint:ofe|u|https://www.fourthcoffee.com/AllHandsDeck.ppt
New Document from Template
The following command will cause the application to create and open a new document based on the template stored at the specified URI. The template file is not modified in this process. An additional command argument may be supplied to specify the default path offered as a save location when the file is first saved. It is possible for the user to choose a different location.
Command Name: nft
Command argument descriptor 1: u
Command argument 1: a URI to the template, based on the http or https scheme
Optional Command argument descriptor 2: s
Optional Command argument 2: URI to specify the default save folder
Example: ms-word:nft|u|https://cohowinery/templates/elegance.pot|s|https://cohowinery/presentations
As a note, if the optional default save location is supplied, it must be pointing to the same host name as the template.
Additionally, the SharePoint Designer and InfoPath applications (which implement the ms-spd: scheme and ms-infopath: schemes, respectively) do not support the 'new document from template' functionality.
1.6 BACKWARDS COMPATIBILITY
When parsing a URI to extract the appropriate command arguments for a given command, the Office URI handler will only use the command arguments that have the expected command argument descriptor. If there are additional pairs of arguments and argument descriptors that have unexpected argument descriptors, they will be removed from the URI. This mechanism allows future versions of the scheme to add additional command arguments without breaking backward compatibility with legacy implementations of this scheme.
1.7 IMPLEMENTATION RESTRICTIONS ON COMMAND ARGUMENTS
The below restrictions are placed on command arguments in its current implementation in Office 2013.
Length limitations on URI command arguments
For URI command arguments, the maximum path length is 256 characters for all apps except Excel, where the limit is 216. Path lengths greater than these may be supported on an app-by-app basis and testing is recommended before deploying any solutions that rely on this.
Allowed characters in URI command arguments
Allowed URIs must conform to the standards proposed in RFC 3987 - Internationalized Resource Identifiers (IRIs) . Characters identified as reserved in RFC 3986 should not be percent encoded. . Filenames must not contain any of the following characters: / : ? < > | ' or *.
APPENDIX A - URI SCHEME REGISTRATION TEMPLATE FOR MS-WORD SCHEME
A-3. URI Scheme Syntax
Word Scheme = 'ms-word:' open-for-edit-cmd | open-for-view-cmd | new-from-template-cmd
open-for-edit-cmd = 'ofe|u|' document-uri
open-for-view-cmd = 'ofv|u|' document-uri
new-from-template-cmd = 'nft|u|' template-uri ['|s|' save-location]
document-uri = URI location of document to open
template-uri = URI location of template file upon which new file will be based
save-location = URI location of folder in which new document should be created
A-4. URI Scheme Semantics
The ms-word scheme defines a URI syntax for opening or creating a word processing document. The scheme defines three commands that serve as instructions regarding what should be done with the referenced document. The commands are 1) open-for-edit-cmd (ofe), which instructs a word processing application to open the document at the specified URI for editing; 2) open-for-view-cmd (ofv), which instructs a word processing application to open the document at the specified URI in a read-only mode; and 3) new-from-template-cmd (nft), which instructs a word processing application to create a new document based on the document template located at the specified template-uri URI and save the new document either in the location specified in the optional save-location URI or, in the absence of that optional URI, in the default document library location.
A-5. Applications/Protocols that use the ms-word URI Scheme
The ms-word URI Scheme is used by Microsoft Office 2013 to invoke Microsoft Word 2013 or Microsoft Word 2010 with Service Pack 2. Microsoft SharePoint 2013 uses ms-word URIs as links to word processing documents stored in SharePoint document libraries.
A-6. Interoperability Considerations
Note that the vertical bar used as a delimiter in this specification is not among those characters identified in section 2.2 of RFC 3986 as reserved for potential use as delimiters.. This is done intentionally to maximize the set of characters the URI command argument can support without a need to percent-encode those characters.
Within < command-argument > segments the RFC 3986 reserved characters ':' and '/' are part of the argument data, not delimiters, and are therefore included unescaped.
A-7. Security Considerations
On systems that have registered handlers to recognize and act on ms-word URIs, clicking on a link to an ms-word URI will cause the registered word processing application to be launched, with instructions to the word processing application to attempt to open a document at the specified URI. Word processing applications registering to process ms-word URIs should implement protections to guard against opening documents from untrusted remote systems that may include malicious code.
A-8. References
RFC 3987 - International Resource Identifiers (IRIs)
APPENDIX B - URI SCHEME REGISTRATION TEMPLATE FOR MS-POWERPOINT SCHEME
B-3. URI Scheme Syntax
PowerPoint Scheme = 'ms-powerpoint:' open-for-edit-cmd | open-for-view-cmd | new-from-template-cmd
open-for-edit-cmd = 'ofe|u|' document-uri
open-for-view-cmd = 'ofv|u|' document-uri
new-from-template-cmd = 'nft|u|' template-uri ['|s|' save-location]
document-uri = URI location of document to open
template-uri = URI location of template file upon which new file will be based
save-location* = URI location of folder in which new document should be created
*save-location is an optional parameter
B-4. URI Scheme Semantics
The ms-powerpoint scheme defines a URI syntax for opening or creating a presentation document. The scheme defines three commands that serve as instructions regarding what should be done with the referenced document. The commands are 1) open-for-edit-cmd (ofe), which instructs a presentation application to open the document at the specified URI for editing; 2) open-for-view-cmd (ofv), which instructs a presentation application to open the document at the specified URI in a read-only mode; and 3) new-from-template-cmd (nft), which instructs a presentation application to create a new document based on the document template located at the specified template-uri URI and save the new document either in the location specified in the optional save-location URI or, in the absence of that optional URI, in the default document library location.
B-5. Applications/Protocols that use the ms-powerpoint URI Scheme
The ms-powerpoint URI Scheme is used by Microsoft Office 2013 to invoke Microsoft PowerPoint 2013 or Microsoft PowerPoint 2010 with Service Pack 2. Microsoft SharePoint 2013 uses ms-powerpoint URIs as links to presentation documents stored in SharePoint document libraries.
B-6. Interoperability Considerations
Note that the vertical bar used as a delimiter in this specification is not among those characters identified in section 2.2 of RFC 3986 as reserved for potential use as delimiters. This is done intentionally to maximize the set of characters the URI command argument can support without a need to percent-encode those characters.
Within < command-argument > segments the RFC 3986 reserved characters ':' and '/' are part of the argument data, not delimiters, and are therefore included unescaped.
B-7. Security Considerations
On systems that have registered handlers to recognize and act on ms-powerpoint URIs, clicking on a link to an ms-powerpoint URI will cause the registered presentation application to be launched, with instructions to the application to attempt to open a document at the specified URI. Applications registering to process ms-powerpoint URIs should implement protections to guard against opening documents from untrusted remote systems that may include malicious code.
B-8. References
RFC 3987 - International Resource Identifiers (IRIs)
APPENDIX C - URI SCHEME REGISTRATION TEMPLATE FOR MS-EXCEL SCHEME
C-3. URI Scheme Syntax
Excel Scheme = 'ms-excel:' open-for-edit-cmd | open-for-view-cmd | new-from-template-cmd
open-for-edit-cmd = 'ofe|u|' document-uri
open-for-view-cmd = 'ofv|u|' document-uri
new-from-template-cmd = 'nft|u|' template-uri ['|s|' save-location]
document-uri = URI location of document to open
template-uri = URI location of template file upon which new file will be based
save-location* = URI location of folder in which new document should be created
*save-location is an optional parameter
C-4. URI Scheme Semantics
The ms-excel scheme defines a URI syntax for opening or creating a spreadsheet document. The scheme defines three commands that serve as instructions regarding what should be done with the referenced document. The commands are 1) open-for-edit-cmd (ofe), which instructs a spreadsheet application to open the document at the specified URI for editing; 2) open-for-view-cmd (ofv), which instructs a spreadsheet application to open the document at the specified URI in a read-only mode; and 3) new-from-template-cmd (nft), which instructs a spreadsheet application to create a new document based on the document template located at the specified template-uri URI and save the new document either in the location specified in the optional save-location URI or, in the absence of that optional URI, in the default document library location.
C-5. Applications/Protocols that use the ms-excel URI Scheme
The ms-excel URI Scheme is used by Microsoft Office 2013 to invoke Microsoft Excel 2013 or Microsoft Excel 2010 with Service Pack 2. Microsoft SharePoint 2013 uses ms-excel URIs as links to spreadsheet documents stored in SharePoint document libraries.
C-6. Interoperability Considerations
Note that the vertical bar used as a delimiter in this specification is not among those characters identified in section 2.2 of RFC 3986 as reserved for potential use as delimiters. This is done intentionally to maximize the set of characters the URI command argument can support without a need to percent-encode those characters.
Within < command-argument > segments the RFC 3986 reserved characters ':' and '/' are part of the argument data, not delimiters, and are therefore included unescaped.
C-7. Security Considerations
On systems that have registered handlers to recognize and act on ms-excel URIs, clicking on a link to an ms-excel URI will cause the registered spreadsheet application to be launched, with instructions to the application to attempt to open a document at the specified URI. Applications registering to process ms-excel URIs should implement protections to guard against opening documents from untrusted remote systems that may include malicious code.
C-8. References
RFC 3987 - International Resource Identifiers (IRIs)
APPENDIX D - URI SCHEME REGISTRATION TEMPLATE FOR MS-VISIO SCHEME
D-3. URI Scheme Syntax
Visio Scheme = 'ms-visio:' open-for-edit-cmd | open-for-view-cmd | new-from-template-cmd
open-for-edit-cmd = 'ofe|u|' document-uri
open-for-view-cmd = 'ofv|u|' document-uri
new-from-template-cmd = 'nft|u|' template-uri ['|s|' save-location]
document-uri = URI location of document to open
template-uri = URI location of template file upon which new file will be based
save-location* = URI location of folder in which new document should be created
*save-location is an optional parameter
D-4. URI Scheme Semantics
The ms-visio scheme defines a URI syntax for opening or creating a Microsoft Visio document. The scheme defines three commands that serve as instructions regarding what should be done with the referenced document. The commands are 1) open-for-edit-cmd (ofe), which instructs Visio to open the document at the specified URI for editing; 2) open-for-view-cmd (ofv), which instructs Visio to open the document at the specified URI in a read-only mode; and 3) new-from-template-cmd (nft), which instructs Visio to create a new document based on the document template located at the specified template-uri URI and save the new document either in the location specified in the optional save-location URI or, in the absence of that optional URI, in the default document library location.
D-5. Applications/Protocols that use the ms-visio URI Scheme
The ms-visio URI Scheme is used by Microsoft Office 2013 to invoke Microsoft Visio 2013 or Microsoft Visio 2010 with Service Pack 2. Microsoft SharePoint 2013 uses ms-visio URIs as links to Visio documents stored in SharePoint document libraries.
D-6. Interoperability Considerations
Note that the vertical bar used as a delimiter in this specification is not among those characters identified in section 2.2 of RFC 3986 as reserved for potential use as delimiters. This is done intentionally to maximize the set of characters the URI command argument can support without a need to percent-encode those characters.
Within < command-argument > segments the RFC 3986 reserved characters ':' and '/' are part of the argument data, not delimiters, and are therefore included unescaped.
D-7. Security Considerations
On systems that have registered handlers to recognize and act on ms-visio URIs, clicking on a link to an ms-visio URI will cause the registered application to be launched, with instructions to the application to attempt to open a document at the specified URI. Applications registering to process ms-visio URIs should implement protections to guard against opening documents from untrusted remote systems that may include malicious code.
D-8. References
RFC 3987 - International Resource Identifiers (IRIs)
APPENDIX E - URI SCHEME REGISTRATION TEMPLATE FOR MS-ACCESS SCHEME
E-3. URI Scheme Syntax
Access Scheme = 'ms-access:' open-for-edit-cmd | open-for-view-cmd | new-from-template-cmd
open-for-edit-cmd = 'ofe|u|' document-uri
open-for-view-cmd = 'ofv|u|' document-uri
new-from-template-cmd = 'nft|u|' template-uri ['|s|' save-location]
document-uri = URI location of document to open
template-uri = URI location of template file upon which new file will be based
save-location* = URI location of folder in which new document should be created
*save-location is an optional parameter
E-4. URI Scheme Semantics
The ms-access scheme defines a URI syntax for opening or creating a database. The scheme defines three commands that serve as instructions regarding what should be done with the referenced database file. The commands are 1) open-for-edit-cmd (ofe), which instructs the database application to open the database at the specified URI for editing; 2) open-for-view-cmd (ofv), which instructs the database application to open the database at the specified URI in a read-only mode; and 3) new-from-template-cmd (nft), which instructs the database application to create a new database based on the template located at the specified template-uri URI and save the new database either in the location specified in the optional save-location URI or, in the absence of that optional URI, in the default document library location.
E-5. Applications/Protocols that use the ms-access URI Scheme
The ms-access URI Scheme is used by Microsoft Office 2013 to invoke Microsoft Access 2013 or Microsoft Access 2010 with Service Pack 2 from web pages. Microsoft SharePoint 2013 uses ms-access URIs as links to Access databases stored in SharePoint document libraries.
E-6. Interoperability Considerations
Note that the vertical bar used as a delimiter in this specification is not among those characters identified in section 2.2 of RFC 3986 as reserved for potential use as delimiters. This is done intentionally to maximize the set of characters the URI command argument can support without a need to percent-encode those characters. Within <command-argument> segments the RFC 3986 reserved characters ':' and '/' are part of the argument data, not delimiters, and are therefore included unescaped.
E-7. Security Considerations
On systems that have registered handlers to recognize and act on ms-access URIs, clicking on a link to an ms-access URI will cause the registered application to be launched, with instructions to the application to attempt to open a database at the specified URI. Applications registering to process ms-access URIs should implement protections to guard against opening databases from untrusted remote systems that may include malicious code.
E-8. References
RFC 3987 - International Resource Identifiers (IRIs)
APPENDIX F - URI SCHEME REGISTRATION TEMPLATE FOR MS-PROJECT SCHEME
F-3. URI Scheme Syntax
Project Scheme = 'ms-project:' open-for-edit-cmd | open-for-view-cmd | new-from-template-cmd
open-for-edit-cmd = 'ofe|u|' document-uri
open-for-view-cmd = 'ofv|u|' document-uri
new-from-template-cmd = 'nft|u|' template-uri ['|s|' save-location]
document-uri = URI location of document to open
template-uri = URI location of template file upon which new file will be based
save-location* = URI location of folder in which new document should be created
*save-location is an optional parameter
F-4. URI Scheme Semantics
The ms-project scheme defines a URI syntax for opening or creating a Microsoft Project document. The scheme defines three commands that serve as instructions regarding what should be done with the referenced document. The commands are 1) open-for-edit-cmd (ofe), which instructs Project to open the document at the specified URI for editing; 2) open-for-view-cmd (ofv), which instructs Project to open the document at the specified URI in a read-only mode; and 3) new-from-template-cmd (nft), which instructs Project to create a new document based on the document template located at the specified template-uri URI and save the new document either in the location specified in the optional save-location URI or, in the absence of that optional URI, in the default document library location.
F-5. Applications/Protocols that use the ms-project URI Scheme
The ms-project URI Scheme is used by Microsoft Office 2013 to invoke Microsoft Project 2013 from web pages. Microsoft SharePoint 2013 uses ms-project URIs as links to Project documents stored in SharePoint document libraries.
F-6. Interoperability Considerations
Note that the vertical bar used as a delimiter in this specification is not among those characters identified in section 2.2 of RFC 3986 as reserved for potential use as delimiters. This is done intentionally to maximize the set of characters the URI command argument can support without a need to percent-encode those characters.
Set Password For Ms Excel
Within < command-argument > segments the RFC 3986 reserved characters ':' and '/' are part of the argument data, not delimiters, and are therefore included unescaped.
F-7. Security Considerations
On systems that have registered handlers to recognize and act on ms-project URIs, clicking on a link to an ms-project URI will cause the registered application to be launched, with instructions to the application to attempt to open a document at the specified URI. Applications registering to process ms-project URIs should implement protections to guard against opening documents from untrusted remote systems that may include malicious code.
F-8. References
RFC 3987 - International Resource Identifiers (IRIs)
APPENDIX G - URI SCHEME REGISTRATION TEMPLATE FOR MS-PUBLISHER SCHEME
G-3. URI Scheme
Syntax Publisher Scheme = 'ms-publisher:' open-for-edit-cmd | open-for-view-cmd | new-from-template-cmd
open-for-edit-cmd = 'ofe|u|' document-uri
open-for-view-cmd = 'ofv|u|' document-uri
new-from-template-cmd = 'nft|u|' template-uri ['|s|' save-location]
document-uri = URI location of document to open
template-uri = URI location of template file upon which new file will be based
save-location* = URI location of folder in which new document should be created
Excel Set Up
*save-location is an optional parameter
G-4. URI Scheme Semantics
The ms-publisher scheme defines a URI syntax for opening or creating a Microsoft Publisher document. The scheme defines three commands that serve as instructions regarding what should be done with the referenced document. The commands are 1) open-for-edit-cmd (ofe), which instructs Publisher to open the document at the specified URI for editing; 2) open-for-view-cmd (ofv), which instructs Publisher to open the document at the specified URI in a read-only mode; and 3) new-from-template-cmd (nft), which instructs Publisher to create a new document based on the document template located at the specified template-uri URI and save the new document either in the location specified in the optional save-location URI or, in the absence of that optional URI, in the default document library location.
G-5. Applications/Protocols that use the ms-publisher URI Scheme
The ms-publisher URI Scheme is used by Microsoft Office 2013 to invoke Microsoft Publisher 2013 or Microsoft Publisher 2010 with Service Pack 2 from web pages. Microsoft SharePoint 2013 uses ms-publisher URIs as links to Publisher documents stored in SharePoint document libraries.
G-6. Interoperability Considerations
Note that the vertical bar used as a delimiter in this specification is not among those characters identified in section 2.2 of RFC 3986 as reserved for potential use as delimiters. This is done intentionally to maximize the set of characters the URI command argument can support without a need to percent-encode those characters. Within <command-argument> segments the RFC 3986 reserved characters ':' and '/' are part of the argument data, not delimiters, and are therefore included unescaped.
G-7. Security Considerations
On systems that have registered handlers to recognize and act on ms-publisher URIs, clicking on a link to an ms-publisher URI will cause the registered application to be launched, with instructions to the application to attempt to open a document at the specified URI. Applications registering to process ms-publisher URIs should implement protections to guard against opening documents from untrusted remote systems that may include malicious code.
G-9. References
RFC 3987 - International Resource Identifiers (IRIs)
APPENDIX H - URI SCHEME REGISTRATION TEMPLATE FOR MS-SPD SCHEME
H-3. URI Scheme Syntax
SharePoint Designer Scheme = 'ms-spd:' open-for-edit-cmd
open-for-edit-cmd = 'ofe|u|' document-uri
document-uri = URI location of document to open
H-4. URI Scheme Semantics
The ms-spd scheme defines a URI syntax for opening a Microsoft SharePoint Designer document. The scheme defines two commands that serve as instructions regarding what should be done with the referenced document. The commands are 1) open-for-edit-cmd (ofe), which instructs SharePoint Designer to open the document at the specified URI for editing; and 2) open-for-view-cmd (ofv), which instructs SharePoint Designer to open the document at the specified URI in a read-only mode.
H-5. Applications/Protocols that use the ms-spd URI Scheme
The ms-spd URI Scheme is used by Microsoft Office 2013 to invoke Microsoft SharePoint Designer 2013 from web pages. Microsoft SharePoint 2013 uses ms-spd URIs as links to SharePoint Designer documents stored in SharePoint document libraries.
H-6. Interoperability Considerations
Note that the vertical bar used as a delimiter in this specification is not among those characters identified in section 2.2 of RFC 3986 as reserved for potential use as delimiters. This is done intentionally to maximize the set of characters the URI command argument can support without a need to percent-encode those characters.
Within < command-argument > segments the RFC 3986 reserved characters ':' and '/' are part of the argument data, not delimiters, and are therefore included unescaped.
H-7. Security Considerations
On systems that have registered handlers to recognize and act on ms-spd URIs, clicking on a link to an ms-spd URI will cause the registered application to be launched, with instructions to the application to attempt to open a document at the specified URI. Applications registering to process ms-spd URIs should implement protections to guard against opening documents from untrusted remote systems that may include malicious code.
H-8. References
RFC 3987 - International Resource Identifiers (IRIs)
APPENDIX I - URI SCHEME REGISTRATION TEMPLATE FOR MS-INFOPATH SCHEME
I-3. URI Scheme Syntax
Infopath Scheme = 'ms-infopath:' open-for-edit-cmd | open-for-view-cmd
open-for-edit-cmd = 'ofe|u|' document-uri
open-for-view-cmd = 'ofv|u|' document-uri
Ms Excel Download For Laptop
document-uri = URI location of document to open
I-4. URI Scheme Semantics
The ms-infopath scheme defines a URI syntax for opening or creating a Microsoft Infopath document. The scheme defines two commands that serve as instructions regarding what should be done with the referenced document. The commands are 1) open-for-edit-cmd (ofe), which instructs InfoPath to open the document at the specified URI for editing; and 2) open-for-view-cmd (ofv), which instructs InfoPath to open the document at the specified URI in a read-only mode.
I-5. Applications/Protocols that use the ms-infopath URI Scheme
The ms-infopath URI Scheme is used by Microsoft Office 2013 to invoke Microsoft Infopath 2013 from web pages. Microsoft SharePoint 2013 uses ms-infopath URIs as links to Infopath documents stored in SharePoint document libraries.
I-6. Interoperability Considerations
Note that the vertical bar used as a delimiter in this specification is not among those characters identified in section 2.2 of RFC 3986 as reserved for potential use as delimiters. This is done intentionally to maximize the set of characters the URI command argument can support without a need to percent-encode those characters.
Within < command-argument > segments the RFC 3986 reserved characters ':' and '/' are part of the argument data, not delimiters, and are therefore included unescaped.
Set Delimiter Ms Excel
I-7. Security Considerations
On systems that have registered handlers to recognize and act on ms-infopath URIs, clicking on a link to an ms-infopath URI will cause the registered application to be launched, with instructions to the application to attempt to open a document at the specified URI. Applications registering to process ms-infopath URIs should implement protections to guard against opening documents from untrusted remote systems that may include malicious code.
I-8. References
RFC 3987 - International Resource Identifiers (IRIs)
-->Note
Office 365 ProPlus is being renamed to Microsoft 365 Apps for enterprise. For more information about this change, read this blog post.

For a Microsoft Excel 2001 for Mac version of this article, see 259921.
Summary
This step-by-step article describes how to use the Microsoft Excel startup folders. Excel uses startup folders in two ways:
- To load Excel workbooks at startup.
- As a reference location for templates.
The actual startup folder locations vary, depending on which version of Excel you use.
Folders that Excel uses at startup
If you install Excel in the default location, Excel opens files from the following paths:
In Microsoft Office Excel 2003, the path is C:Program FilesMicrosoft OfficeOffice11Xlstart
In Microsoft Office Excel 2007, the path is C:Program FilesMicrosoft OfficeOffice12Xlstart
C:Documents and SettingsUser_nameApplication DataMicrosoftExcelXLSTART
In this path, User_name is your logon user name.
The folder that is specified in the At startup, open all files in box.
Note
To find the At startup, open all files in box in Excel 2003, click Options on the Toolsmenu, and then click the General tab.
To find the At startup, open all files in box in Excel 2007, click the Microsoft Office Button, click Excel Options, and then click Advanced. The At startup, open all files in box is under General.
Accepted file types during Excel startup
You typically use startup folders to load Excel templates and add-ins. You can also use startup folders to load workbooks. When you load the following types of files from a startup folder, the files have the important characteristics that are described in the following list.
Templates
If you save a workbook named Book.xlt, and then put it in a startup folder location, that workbook is the default workbook when you start Excel or open a new workbook.
To use additional templates, you must save them in the following folder:
C:Program FilesMicrosoft OfficeTemplates1033
To use the templates in Excel 2003, follow these steps:
- On the Filemenu, click New.
- In the New Workbook task pane, click On my computer under Templates.
- In the Templates dialog box, double-click the template for the type of workbook that you want to create on the Spreadsheet Solutions tab.
To use the templates in Excel 2007, follow these steps:
- Click the Microsoft Office Button, and then click New.
- Under Templates, click Installed Templates.
- Under Installed Templates, click the template that you want, and then click Create.
Add-ins
Add-ins (.xla files) that you put in a startup folder do not typically appear when you start Excel. The add-ins are loaded in memory. The add-ins run any auto macros.
You can use these add-ins by whatever method the add-in provides (for example, a command on a menu or a button on a toolbar).
Workbooks
Set Header Ms-excel
Workbooks (.xls files) that you put in a startup folder are loaded and appear when you start Excel, unless the workbook is saved in a hidden state.
For example, the personal macro workbook Personal.xls is a global macro workbook that Excel typically loads from the XLStart folder in a hidden state.
Mcq Set For Ms Excel
Incorrect use of the alternative startup file location
When you use the alternative startup file location, you must specify a file path where there are recognizable file types (such as templates, add-ins, and workbooks).
If Excel finds unrecognizable file types in a startup folder, you may receive an error message. The most common error message is:
This file is not a recognizable format.
Use the default file location
In addition to the alternative startup file location, the default file location can be set by using the Default file location box on the General tab in the Options dialog box in Excel 2003.
The default file location differs from a startup folder. It can set the folder location that you want Excel to point to when you open or save a file by using the File menu.
Note
In Excel 2007, to see the default file location, follow these steps:
- Click the Microsoft Office Button, and then click Excel Options.
- Click Save.
- The Default file location box is under Save workbooks.
